Dealing with Frostbite on Newborn Lambs and Kids by Dr. tatiana Stanton
Dealing with Frostbite on Newborn Lambs and Kids
by tatiana Stanton, Cornell Univ. Small Ruminant Extension Specialist
Does or ewes with cropped ears due to frostbite damage at birth are not an uncommon sight on Northeast goat and sheep farms. Although the condition is not life threatening it leads to interesting explanations in the show ring as to why your Alpine looks like a LaMancha. However in severe winters, frost bite can be far more serious affecting even the feet and tails on newborns as well as the teats on milkers.
Under normal conditions, blood carries oxygen throughout an animal's body to keep all the tissue healthy. However, if the animal's body temperature suddenly starts to drop, its blood vessels constrict to keep the animal alive by diverting blood (and oxygen) away from its extremities and to its vital organs. The lack of blood and oxygen begins to damage the tissue cells in the deprived extremities and ice crystals form. Blood clots may also form further reducing circulation to the damaged tissue. If the condition persists long enough, dry gangrene can occur, leading to the tissue damage and amputations that we associate with frost bite.
 Kid with missing ear tips resulting from frostbite. Click to enlarge.
Kid with missing ear tips resulting from frostbite. Click to enlarge.Extreme body heat loss (hypothermia) is hastened by wind chill and wet animals while excess body fat can help slow heat loss. Thus newborn kids and lambs are particularly vulnerable to hypothermia. Vigorously rubbing and applying direct heat to the body of a chilled lamb or kid can help save its life. However, the same treatment is not advisable for frost bite damage to its extremities. Instead the recommendation is to rapidly thaw the extremities in warm water at about 101 to <105˚ F. This is a little warmer than the inside of your wrist, or about the temperature you warm a bottle of colostrum to when feeding an orphaned newborn. It is then very important to dry the affected extremities before they can freeze again. However, you need to avoid rubbing them or applying direct heat >105˚ F as this may damage the tissue more. Air drying the extremities is easy if you have rushed the newborn to a warm house prior to thawing it out. However in a frigid barn, it is more challenging. Wrapping the extremities in a warm towel (straight out of the dryer) or using a well-padded heating pad are two options. Otherwise, if your only choices are a hair dryer or heat lamp, keep the blowing temperature low, the heat lamp well anchored and keep them a good distance from the affected tissue. Keep in mind that frost bitten areas are very susceptible to sun burn or heat lamp burn. Basically you want to warm the air rather than the tissue itself. Do not bandage the area as this can interfere with circulation. Ears, especially long ears, are most commonly affected. However, in severe subzero temperatures, newborns in a drafty barn can suffer frostbite to tails and legs. If you suspect that frost bite may be more extensive than just an ear or two, be sure to thoroughly thaw and dry legs using the above procedure. Keep in mind that hind legs are more susceptible than front legs as most newborn kids and lambs keep their front legs warm by naturally tucking them under their bodies shortly after birth.
Frost bitten areas are very vulnerable to re-freezing. Therefore if frostbite damage to the legs is suspected, try to house the newborn at temperatures above freezing for the next few days avoiding any rigorous exercise. Recommendations include continuing to warm the affected area in 101 to <105˚ F water twice daily for the next 2 to 3 days. Lanolin, zinc oxide ointment or aloe vera may be gently applied. After a few days, the hair on affected areas may start to shed. The tips of ears may shrivel or swell and eventually all or part of the ear may slough off. If the legs are affected they will swell after a few days and hair and tissue will begin to fall off. When potential leg damage is suspected, talk to your veterinarian to see if he/she wants to prescribe fluids to deal with dehydration to the limbs and/or medicines such as Flunixin meglumine (Banamine©), etc. to manage pain, block the release of inflammatory mediators, or help increase blood circulation. If tissue does start to slough, ask your veterinarian if spraying a liquid bandage onto the affected areas will help protect the sensitive skin and whether antibiotics to prevent secondary infections are indicated. Immediate amputation of the limb is not advised as the hope is that there is only severe tissue damage and no actual gangrene, and the fear is that the gangrene if present may extend farther up the leg than initially anticipated. It can take up to 3 to 6 weeks for a distinct line of demarcation between viable and necrotic tissue to appear. There appears to be very little pain when the distal limb eventually falls off. If the break is below the cannon bone, the animal may develop calluses and get around fairly well on its naked "foot". Depending on where the break is and your farm situation, you and your veterinarian will need to decide whether to euthanize the animal, grow it out to slaughter weight, or keep it as a pet.
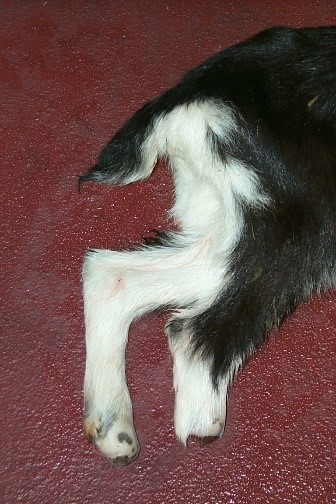 Kid exhibiting missing portions of hooves as a result of frostbite. Click to enlarge.
Kid exhibiting missing portions of hooves as a result of frostbite. Click to enlarge.Dr. Pamela Karner VMD from Starland Veterinary Services has emphasized in the past that "by the time frost bite has been identified in an animal, it is too late to do much. Prevention is the key, wet and cold combined are deadly." When kidding or lambing in winter, make sure your barns are suitable for likely weather conditions. If subzero temperatures and wind chill are predicted, increase the frequency of your birthing checks to ensure that newborns are dried off rapidly after birth, especially on extremities. Increase the depth of your bedding and make sure it stays dry to help keep extremities warm on both mature and young animals. A few cropped ears are inevitable when sheep and goat farming in the Northeast but let's try to keep frostbite from causing more serious damage.
Thank you to Mariah Gentry, Class of 2016, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Ambulatory and Production Medicine for her excellent information about frostbite. Thank you to Dr. Mary Smith, DVM, Professor of Ambulatory and Production Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York for her photos and additional insights.
Upcoming Events
WEBINAR - Automated Milking Systems Efficiency: Balancing Focus on Individual Cows and System Optimization
May 8, 2024
Please join Cornell the SWNY team and MSU Extension for our talk with Dr. Pablo Silva Boloña on improving efficiency of Automated milking systems by focusing on milking settings for individual and group success.
Broiler Field Day at Sunny Cove Farm
June 6, 2024
Alfred Station, NY
Join us for a field day to explore broiler production, processing, and finances. Meghan Snyder of Sunny Cove Farm will be our host. She raises small batches of organic broilers, processing them on-farm under the 1,000 bird exemption.
Stockmanship and Stewardship 2024
October 25, 2024
Hamburg, NY
Save the date!! The event is one of 4 across the US and is a two-day educational experience featuring low-stress cattle handling demonstrations, Beef Quality Assurance educational sessions, facility design sessions, and industry updates.
Announcements
No announcements at this time.





